FUNDING CUTS IMPACT CT HUMANITIES: Help CT Humanities navigate recent funding cuts and continue our vital work across Connecticut. All donations made to CTH will be matched dollar-for-dollar up to $50,000. Donate today!
News & Updates

From Aprons to Lab Coats: The Art and Science of Home Economics
In 1893 the Storrs Agricultural College (the precursor to the University of Connecticut) began training women in domestic science, the discipline that would later be called home economics.
Read
The Deplorable History of Hartford’s Seyms Street Jail
Abhorrent conditions characterized life in Hartford’s Seyms Street Jail for much of its century-long service to the county.
Read
A Diversified Mind: Hiram Percy Maxim
No matter his field of endeavor—from automotive design to wireless radio—this multitalented creator had a hand in key developments of the early 1900s.
Read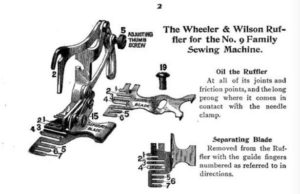
Wheeler & Wilson: A Stitchy Situation in Watertown
The Watertown firm of Wheeler & Wilson Manufacturing produced one of the most successful products of the late 19th century.
Read
Seaside Tuberculosis Sanatorium: Waterford’s Contested Oceanfront Gem
Connecticut’s Seaside Sanatorium in Waterford is the site of a former nationally recognized tuberculosis hospital.
Read
The Importance of Being Puritan: Church and State in Colonial Connecticut
Connecticut Protestants wanted to cleanse the church of what they saw as corruption, and to return to the simplicity and purity of early Christian worship.
Read
Serving Up Justice: Hartford’s Black Workers Organize
The earliest labor union for African American workers in Hartford appeared in 1902 with the birth of the Colored Waiters and Cooks Local 359.
Read
Connecticut Revolutionized Geography – Who Knew?
In 1828, Jesse Olney published A Practical System of Modern Geography, which revolutionized the way the subject was taught in schools during the 19th century.
Read
The Child’s Picture Defining and Reading Book by Thomas Hopkins Gallaudet
Thomas Hopkins Gallaudet The Child’s Picture Defining and Reading Book in 1830 while the principal of the American School for the Deaf in Hartford.
Read
David Humphreys, Soldier, Statesman, and Agricultural Innovator
Despite an accomplished political career, this Derby-born gentleman of means is best remembered for introducing Merino sheep to North America.
Read
Rails and Paper Trails
The railroad first came to Connecticut in August of 1832 when the New York, Providence & Boston Railroad broke ground in Stonington.
Read
The Rev. Amos Beman’s Devotion to Education, Social Activism, and New Haven
Amos Beman spent much of his life a religious leader and social activist in New Haven, fighting the stereotypes and other obstacles he encountered because of his race.
Read
Dinosaur Tracks Found – Today in History: August 23
On August 23, 1966, hundreds of dinosaur tracks were uncovered in Rocky Hill by a bulldozer operator.
Read
Roosevelt Rides in an Electric Car – Today in History: August 22
On August 22, 1902, President Theodore Roosevelt rode through the streets of Hartford in an electric automobile.
Read
The Charter Oak Fell – Today in History: August 21
On August 21, 1856, the Charter Oak, a noted landmark and symbol of Hartford and Connecticut, fell during a severe wind and rain storm.
Read
A Pie Tin’s Soaring Sales
Tins used to hold pies at William Frisbie’s pie company in Bridgeport in the late 1800s reportedly provided the inspiration for Wham-O’s most popular toy, the Frisbee.
Read
Connecticut Servicemen in the “Bloody Bucket” Division
Nicknamed the “Keystone Division,” the United States Army’s 28th Infantry Division came together in 1917 by combining units of the Pennsylvania National Guard.
Read
Governor Jonathan Trumbull Dies – Today in History: August 17
On August 17, 1785, Connecticut’s first governor, Jonathan Trumbull, died.
Read
“’No Taxation without Representation’: Black Voting in Connecticut
In 1870, Connecticut ratified the 15th Amendment, but poll taxes, grandfather clauses, and other means of disenfranchising African Americans remained in place.
Read
Connecticut Draws the Curtain on Public Executions
Brooklyn’s status as county seat in 1831 resulted in the town hosting what is widely accepted as the last public hanging in Connecticut.
Read
Senator Brandegee Stonewalls Women’s Suffrage
Senator Frank Brandegee of New London vehemently opposed progressive legislation at the national level, particularly when it came to the issue of women’s suffrage.
Read
Andover’s Award-Winning Creamery
Started in 1886 by town residents, the Andover Creamery Corporation typified cooperative agricultural enterprises of the late 19th and early 20th centuries.
Read
Defending Connecticut: Fortifying New London Against the British in 1812
“Sir, You will immediately commence the repairs of the magazine at Fort Trumbull and the block house at Fort Griswold…,” wrote the US Secretary of War to a captain in New London.
Read
Connecticut’s Early Commercial Banks
After observing the financial success of commercial banks in Boston and New York City, wealthy elites in Connecticut pressured the Connecticut General Assembly to grant charters for privately owned commercial banks in Hartford, New Haven, and New London in 1792.
Read
The Great Wallingford Tornado – Today in History: August 9
On August 9, 1878, a tornado swept from west to east across the northern part of Wallingford.
Read
Home Missionary Society’s First Missionary – Today in History: August 7
On August 7, 1800, David Bacon, a native of Woodstock and a minister with the Home Missionary Society of Connecticut, set out on foot for the then far lands of the West.
Read
Orange Seeds Yield Corn, Alfafa, Soy, and More
The antecedents of many of today’s most widely utilized crop seeds can trace their lineage back to a company started by the Clark family in Orange, Connecticut.
Read
Washington’s Sister Susie Society
The Sister Susie Society in Washington, Connecticut, started out as a reading circle but became a fundraising and World War I relief organization.
Read
The Danbury Hatters
References to the hat making industry abound in Danbury and continue to shape much of the city’s identity today.
Read
Hall of Flags: Memorial to Connecticut’s Civil War Colors
Battle flags played an important strategic and ceremonial role in Civil War battles. The preservation of Connecticut’s Civil War colors has been a long, delicate, and expensive process.
Read
Lake Pocotopaug Shapes the Growth of East Hampton
East Hampton is home to one of Connecticut’s largest inland bodies of water, Lake Pocotopaug.
Read
Death and Mourning in the Civil War Era
The Civil War transformed traditional practices of death and mourning in Victorian-era Connecticut.
Read
Ralph Earl: Portrait of an Early American Artist
In addition to some of the earliest Revolutionary War battle scenes, Ralph Earl painted prominent figures of the colonial period.
Read
Hope on the Wall: Connecticut’s New Deal Post Office Murals
Between 1934 and 1943, the federal government placed murals in twenty-three Connecticut post offices.
Read
An Old Saybrook Borough has a Stately History
The Borough of Fenwick, a well-known summer community in Old Saybrook, is named for George Fenwick and his family.
Read
Connecticut Valley Railroad’s First Train – Today in History: July 29
On July 29, 1871, a ceremonial train ran along the new 44-mile track built by the Connecticut Valley Railroad.
Read
A Baltic Mill Helps Found a New Town
The Baltic Mill was once the largest cotton mill in the United States and led to the founding of the town of Sprague.
Read
Hartford Wide-Awakes – Today in History: July 26
On July 26, 1860, the Hartford Wide-Awakes welcomed the Newark, New Jersey, Wide-Awakes to a banquet and ratification meeting at Hartford’s City Hall.
Read
Connecticut Valley Style: Eliphalet Chapin Inspires a Tradition of Craft
Favoring local cherry and pine woods, this furniture maker introduced Philadelphia-style flair to New England consumers.
Read
Herbert Abrams Immortalizes the Nation’s Leaders
Herbert Abrams was an American painter whose portraits hang in some of the most prestigious institutions in the country.
Read
The Adventure of a Lifetime: John Ledyard and Captain Cook’s Last Voyage
Published in Hartford in 1783, this book by a Groton-born traveler captured a young nation’s imagination with its tales of discovery.
Read
A World in Motion: Artist and Sculptor Alexander Calder
Most renowned for his invention of the mobile, an abstract sculpture that moves, Calder is considered a pioneer of kinetic art.
Read
Aristocratic Dental Cream Gets Squeezed
Taking advantage of his skills as a dentist and chemist, Dr. Washington Wentworth Sheffield, in 1850 at the age of 23, invented modern toothpaste.
Read
A Unique Island Attraction in Bridgeport
When Bridgeport annexed the borough of West Stratford in 1889, the acquisition came with a a small 37-acre parcel of land on a barrier island at the mouth of Bridgeport Harbor.
Read
Orville Platt Helps Define International Relations after the Spanish-American War
Orville Platt was a powerful Republican senator from Washington, Connecticut. He presented the Platt Amendment to Congress.
Read
Reading, Writing, and the Great Outdoors: Frederick Gunn’s School Transforms Victorian-era Education
In 1850, this educator, prominent abolitionist, and outdoorsman founded The Gunnery, a school in Washington, Connecticut.
Read
Hiram Bingham IV: A Humanitarian Honored for Saving Lives during WWII
Career diplomat Hiram Bingham IV, whose family has lived in Salem, Connecticut, for generations, was born in 1903.
Read
The White Mountain Express Derails in Greenwich
On July 16, 1908, the gong of the ambulances on Greenwich Avenue broadcast one of the worst accidents on the New York, New Haven and Hartford Railroad.
Read
Creating Candlewood Lake – Today in History: July 15
Candlewood Lake was the first large-scale project in the United States to employ the concept of a pumped-water storage facility.
Read
Did You Know a Connecticut Governor Was a US Spy?
In late 1943 James Lukens McConaughy became Deputy Director in Charge of Schools and Training for the precursor of the Central Intelligence agency.
ReadMore Articles




