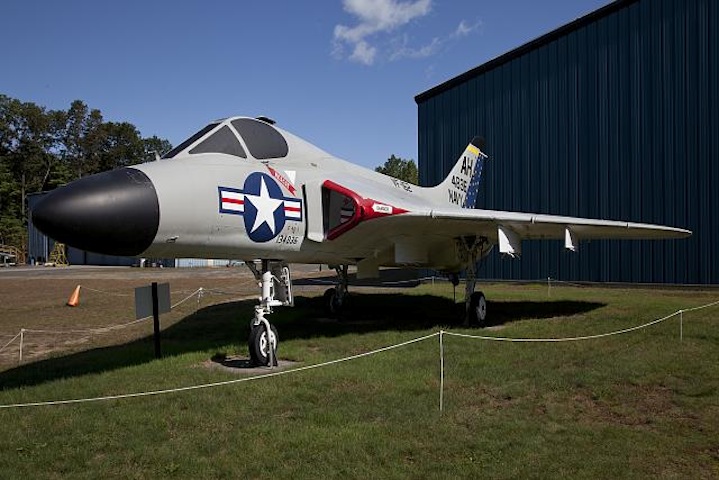
Carol Highsmith, New England Air Museum (NEAM) at Bradley International Airport, Windsor Locks, Connecticut – Library of Congress, Prints and Photographs Division, The George F. Landegger Collection of Connecticut Photographs in the Carol M. Highsmith’s America
The Hartford County town of Windsor Locks sits on the Connecticut River’s west bank, roughly halfway between Hartford and Springfield, Massachusetts. Originally part of Windsor, Windsor Locks incorporated in 1854. At the southern end of the Enfield Falls Canal, which opened in 1829, the town took part of its name from the locks. These controlled water levels in the canal and allowed vessels to safely bypass a dangerously shallow stretch of the river. Industry also sprung up in town and with it a vibrant working-class community. Windsor Locks’ native Ella Grasso, who became Connecticut’s first woman governor in 1975, hailed from such roots. Today, as home to Bradley International Airport, Windsor Locks remains a vital transportation hub.
Featured
Bradley International Airport Transforms Windsor Locks into Regional Gateway
Bradley International Airport in Windsor Locks is Connecticut’s largest airport and the second largest in New England. …[more]